Cardiac catheterization
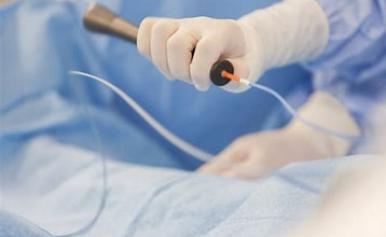
Cardiac catheterization (also called cardiac cath, heart cath, or coronary angiogram) is a procedure that allows your doctor to see how well your blood vessels supply your heart. During the test, they put a long, narrow tube called a catheter into a blood vessel in your arm or leg and guide it to your heart with the aid of a special X-ray machine. Doctors use contrast dye that they inject into your blood vessel through the catheter to create X-ray videos of your valves, coronary arteries, and heart chambers.
-
Cardiac catheterization
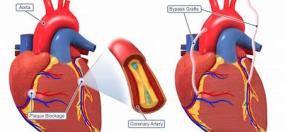
Your doctor inserts a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip. When this balloon is inflated, it pushes plaque out and widens your artery.Your doctor inserts a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip. When this balloon is inflated, it pushes plaque out and widens your artery.Your doctor inserts a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip. When this balloon is inflated, it pushes plaque out and widens your artery.Your doctor inserts a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip. When this balloon is inflated, it pushes plaque out and widens your artery.Your doctor inserts a catheter with a tiny balloon at the tip. When this balloon is inflated, it pushes plaque out and widens your artery.
-
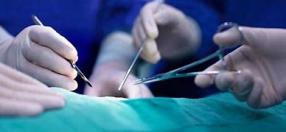
Biopsy. Y
A cardiac cath is generally safe. But as with any procedure that involves going into your body, there are risks. Your doctor will discuss the risks with you and be careful to lessen the chances of having them.
.